T2 Biosystems
Our T2Bacteria® and T2Candida® Panels run on the automated T2Dx® Instrument. They are the first and only FDA-cleared blood tests that identify sepsis-causing pathogens without the wait for blood culture.

T2Dx Instrument
Breakthrough technology enabling direct detection from whole blood
The FDA-cleared T2Dx Instrument is fully automated, walk away, clinical multiplex benchtop diagnostic system capable of running tests directly from whole blood.
The benefits of the T2Dx Instrument include
- Rapid results
- Easy to operate
- Performs with 4 mL whole blood (No blood culture)
- Random access
- Simple user interface
- One instruments, multiple tests
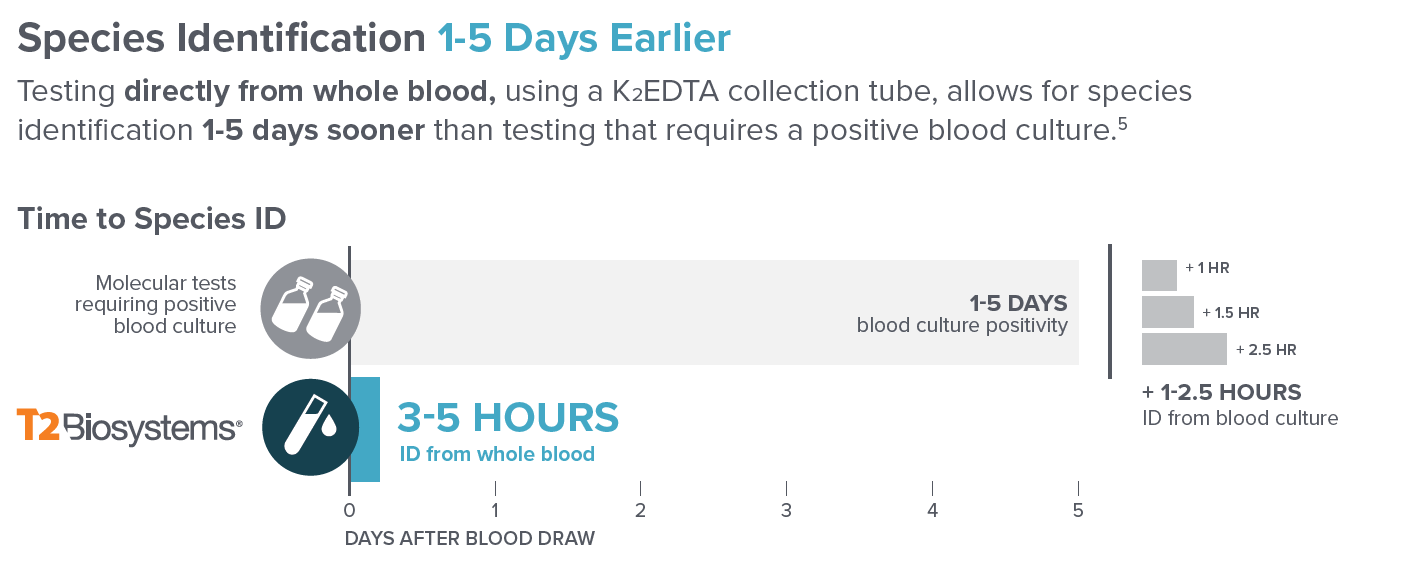
“(5). Peker, N., et al. Table 1. Clin Microb &Inf, 2018.”

T2Bacteria Panel
Enhance the standard of care for sepsis — by detecting bloodstream infections sooner
The T2Bacteria® Panel is the first and only FDA-cleared and CE-marked panel to detect five clinically relevant bacterial pathogens in 3 to 5 hours, directly from a whole blood sample. E. faecium, S. aureus, K. pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa, and E. coli represent the majority of bacteremia seen in the emergency department and those causing hospital-acquired infections. In addition, several of these species are known as ESKAPE pathogens, characterized as virulent and difficult to treat with empiric antimicrobial therapy, making faster species identification and targeted treatment critical to improving patient outcomes.
The positive clinical impact of T2Bacteria
- Target therapy sooner by reducing the time to species ID
- Increase clinician confidence in treatment with accurate and reliable results
- Impact patient outcomes and reduce length of stay for patients with bloodstream infections
- Improve antimicrobial stewardship
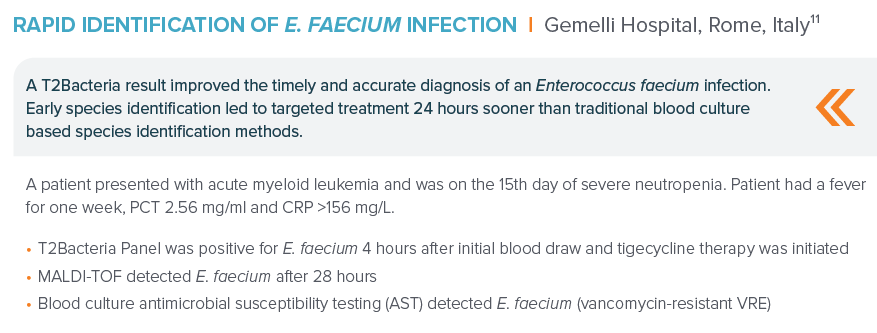
“(11). DeAngelis, Presentation ECCMID 2019.”
T2Candida Panel
Faster targeted therapy leads to reduced costs and improved outcomes
The T2Candida® Panel is the first and only FDA-cleared diagnostic test for the detection of sepsis-causing fungal pathogens, direct from whole blood. Species identification is provided within 3 to 5 hours of the first blood draw and independent of a positive blood culture, often before the second dose of antimicrobials is administered.
The positive clinical impact of T2Candida
- Better patient outcomes
- Unprecedented speed and accuracy
- Faster targeted therapy
- Improved stewardship and pharmacy savings

“(10). Snyder J, World Microbe Forum: Industry & Science Symposium.2021.”
1. In 2,731 septic shock patients, during the first 6 hours of hospital care, every hour delaying effective antimicrobial therapy reduced survival by 7.6%.
2. In 111,816 patients given a New York state-mandated sepsis bundle, every hour delaying appropriate antibiotic therapy increased odds of death by 4.0% .
In a meta-analysis of 70 studies, compared to patients given an appropriate empiric antibiotic therapy, patients given inappropriate empiric antibiotics showed over two-times higher odds of death. These studies support that rapid and targeted therapy to treat bacteremia and sepsis saves lives.
CONTACT NOW
Are you interested in the product?
We’d love to hear from you. Get in touch with us just below to request an offer!

